NOS Network Operating System |Definition, Examples, Types, Functions, Advantages and Disadvantages
Published: 24 Oct 2024
What is a Network Operating System?
A Network Operating System (NOS) is a special type of software that helps computers connect and communicate with each other over a network. It allows different devices, like computers and printers, to share resources and data easily. A NOS is mainly used in businesses or organizations to manage and control network operations, making it simpler to handle tasks like file sharing, security, and user access.
Examples of Network Operating System
Here are some examples of Network Operating Systems:
- Windows Server: This is a version of Windows designed to manage networks, share files, and control access to computers in a network.
- Linux-based Network OS (like Ubuntu Server): Linux versions made for network management, used for running web servers, controlling users, and sharing resources.
- Novell NetWare: An older network OS that helped organizations connect and share files, but it’s less common now.
- Unix-based Network OS: Used by large organizations to manage networks, known for being powerful and secure.
- MacOS Server: A version of macOS designed to manage networks for Apple devices like iMacs and MacBooks.
Types of Network Operating System
The important types of network operating systems include peer-to-peer networks, client-server networks, distributed networks, real-time networks, and multiprocessor networks.
Peer-to-Peer Network OS
A Peer-to-Peer Network OS allows all computers in the network to connect and share resources directly without a central server. Each computer can act as both a client and a server, making it simple and cost-effective. This type of network is often used in small setups like homes or small offices where all devices can easily share files or printers.
Client-Server Network OS
A Client-Server Network OS uses a central computer, called the server, to manage and provide resources like files and security to other computers, known as clients. The server controls everything, while clients request services. This setup is commonly used in larger businesses or organizations for better control and security over the network.
Distributed Network OS
A Distributed Network OS connects multiple computers to work together as a single system. It spreads tasks across different machines, which helps balance the workload and improves efficiency. This type of network allows computers to share resources and collaborate, making it ideal for larger systems that need to handle a lot of data.
Real-Time Network OS
A Real-Time Network OS is designed to process data and respond instantly or quickly. It is used in systems where timing is crucial, like air traffic control or medical devices, where delays can have serious consequences. This type of operating system ensures that tasks are completed within strict time limits to maintain safety and efficiency.
Multiprocessor Network OS
A Multiprocessor Network OS allows multiple processors (or CPUs) to work together within a single computer to enhance performance. This setup helps handle complex tasks and speeds up data processing, making it ideal for systems that require high computing power. It’s commonly used in applications like scientific research, where large amounts of data need to be processed quickly and efficiently.
Functions of the NOS (Network Operating System)
Here are the five main functions of a Network Operating System:
- Resource Sharing: NOS allows computers in the network to share resources like files, printers, and internet connections. This makes it easier for users to access what they need without having to rely on their own devices alone.
- User Management: The NOS helps manage user accounts and permissions. It controls who can access certain files or resources, ensuring that only authorized users can get in.
- Data Communication: A NOS enables computers to communicate with each other over the network. It manages data transfer between devices, ensuring messages and files are sent and received correctly.
- Security Management: The NOS provides security features to protect the network from unauthorized access and threats. It helps set up firewalls, passwords, and encryption to keep data safe.
- Network Management: NOS monitors and controls the overall network performance. It helps troubleshoot issues, manage traffic, and ensure that everything is running smoothly for all users.
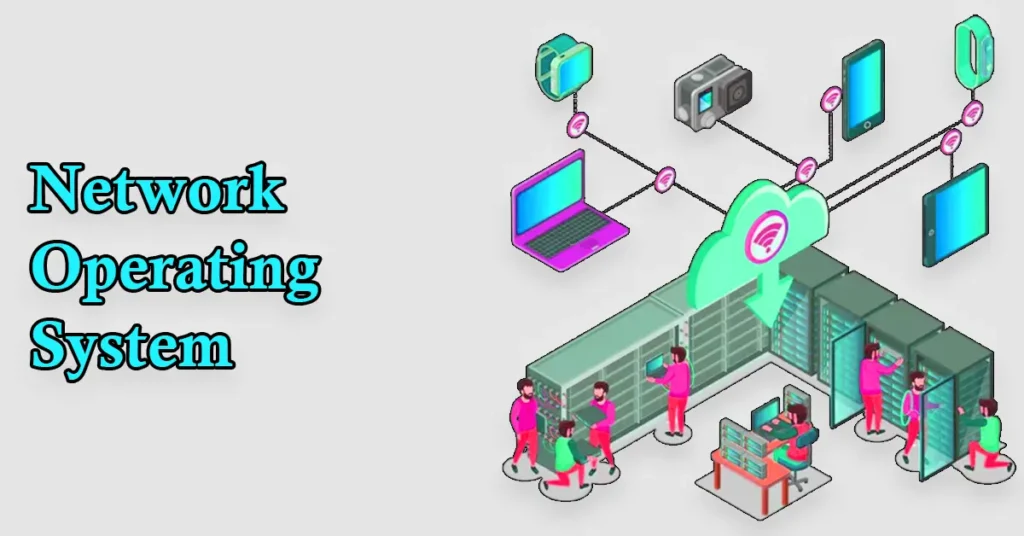
Why do network operators need an NOS?
Network operators need a Network Operating System (NOS) to effectively manage and control their networks. The NOS helps them oversee user accounts, share resources like files and printers, and ensure that all devices can communicate smoothly. With a centralized system, operators can easily monitor network performance and troubleshoot issues as they arise.
Additionally, a NOS provides essential security features to protect the network from unauthorized access and threats. It helps set up user permissions, encrypt data, and maintain overall network safety. By using an NOS; network operators can create a reliable and efficient network environment that supports the needs of users and enhances productivity.
History of Network Operating Systems (NOS)
The history of Network Operating Systems (NOS) began in the 1970s and 1980s when computers started to connect and communicate with each other. Early networks used simple systems to share files and printers, but these lacked central control and security features.
In the late 1980s, more sophisticated NOSs, such as Novell NetWare, were developed. These allowed multiple computers to share resources and manage user access effectively, marking a significant improvement in network management and performance.
In the 1990s, Microsoft introduced Windows NT, which combined networking capabilities with a user-friendly interface, making it popular among businesses. As the internet grew in the late 1990s and early 2000s, NOSs evolved to support larger networks and enhanced security features.
Today, NOSs are essential for managing complex networks in organizations of all sizes. They continue with technological advancements, offering better performance, security, and scalability to meet the needs of modern users.
Features of Network Operating Systems
- File and Resource Sharing: NOS allows computers in a network to share files, printers, and other resources easily. This feature enables users to access shared documents and use common devices without needing to transfer files manually between computers.
- User Management and Security: A NOS helps manage user accounts and permissions, ensuring that only authorized users can access specific files and resources. This feature includes setting up passwords and access controls to protect sensitive information from unauthorized access.
- Network Monitoring and Performance Management: NOS provides tools to monitor network performance and troubleshoot issues. This feature helps network administrators keep an eye on traffic, detect problems, and ensure that everything runs smoothly for all users.
Advantages of Network Operating Systems
- Resource Sharing: NOS allows multiple computers to share resources like files, printers, and internet connections. This makes it easier for users to access what they need without having to rely on their individual devices, improving collaboration and productivity.
- Centralized Management: With NOS, network administrators can manage all user accounts, security settings, and resources from a single location. This central control simplifies the management process, making maintaining and troubleshooting the network easier.
- Improved Security: NOS offers built-in security features that help protect the network from unauthorized access and threats. By managing user permissions and using encryption, sensitive data is kept safe and ensures that only authorized users can access important information.
- Scalability: Network Operating Systems are designed to grow with an organization. They allow for the easy addition of new computers and devices without disrupting existing services, making it simple to expand the network as needs change.
- Enhanced Communication: NOS facilitates smooth communication between connected devices. This enables users to send messages, share files, and collaborate in real-time, leading to better teamwork and faster decision-making within the organization.
Disadvantages of Network Operating Systems
- Cost: Setting up a Network Operating System can be expensive. It often requires purchasing specialized software, hardware, and licenses, which can add up, especially for small businesses or organizations.
- Complexity: NOS can be complex to set up and manage. Network administrators need to have technical skills to configure the system, manage users, and troubleshoot issues, which can be a challenge for those without IT expertise.
- Security Risks: While NOS offers security features, it can still be vulnerable to hacking and cyber-attacks. If not properly managed, unauthorized users may gain access to sensitive information, leading to potential data breaches.
- Single Point of Failure: In a client-server model, if the central server fails, it can disrupt the entire network. This means that all users may lose access to shared resources, causing delays and loss of productivity until the server is fixed.
- Maintenance Requirements: NOS requires regular updates and maintenance to ensure optimal performance and security. This can involve time and effort from IT staff, which can be challenging for smaller organizations with limited resources.
Conclusion about NOS in Networking
Network Operating Systems (NOS) play a crucial role in managing and connecting computers within a network. They enable resource sharing, improve security, and allow for centralized management, making it easier for organizations to operate efficiently. While NOS comes with some challenges, such as cost and complexity, the benefits they provide—like enhanced communication and scalability—make them essential for businesses of all sizes. As technology continues to evolve, NOS will remain vital for ensuring that networks run smoothly and securely, supporting the needs of users and organizations alike.
FAQS – NOS Network
The full form of NOS is Network Operating System.
The role of Network Operations is to manage and maintain a network. This includes ensuring all devices are connected, monitoring performance, troubleshooting issues, and keeping the network secure.
A Network Operating System (NOS) is software that helps computers in a network communicate and share resources. It allows users to access files, printers, and other devices while managing security and user permissions.
Five devices used in a network are:
Router: A router is a device that connects different networks and directs data traffic.
Switch: Connects multiple devices within the same network and helps them communicate.
Hub: A basic device that connects multiple computers in a network but without advanced features.
Modem: Connects a network to the internet.
Access Point: Allows wireless devices to connect to a wired network.
The very first Network Operating System was Novell NetWare, which was widely used in the 1980s to allow computers to share resources and communicate over a network.

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks